Overview
-
Status
Ongoing -
Estimated Completion
2024 -
Location
Creston, Iowa -
Grants Received
$40,000 -
Total Budget
$3,290,723 -
Friends Group
High Lakes Outdoor Alliance -
Partners
Iowa Department of Natural Resources, Southern Iowa Rural Water Association
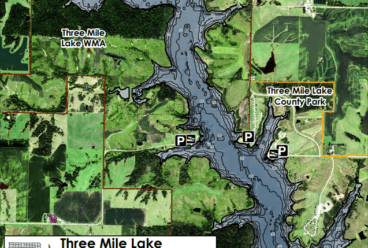
Three-Mile Lake is an 880-acre multi-purpose reservoir located in rural southern Iowa (Figure 1). The lake was constructed in 1995 with a main focus of providing public drinking water to 30 towns and over 13,000 rural water customers. In addition to a public water supply source, the lake offers many recreational opportunities including sailing, powerboating, water skiing, and no-wake areas for fishing. The lake is surrounded by hundreds of acres of wildlife management areas for public hunting and wildlife viewing. The Union County Conservation Board manages a portion of the public land around the lake and provides amenities such as a full-service campground, primitive campground, rental cabins, event lodge, swimming beach, and playground areas providing year-round recreational opportunities.
The objectives of this project are:
- Reduce sedimentation and nutrification in Three-Mile Lake
- Improve the water quality by lessening sedimentation and nitrification in Three-Mile Lake
- Improve the quality of fish habitat available to sportfish in Three-Mile Lake
Why It Matters
Three-Mile Lake rests approximately 10 miles from the city of Creston, Iowa. The Creston area is a very popular area for outdoor recreation. In addition to Three-Mile Lake, Green Valley Lake (379 acres) and Twelve-Mile Creek Lake (640 acres) are all within a 10 mile radius of the city of Creston and provide a significant recreational and economic importance. According to an on-going study by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources’ (DNR) Fisheries Research Section, the Creston area lakes draw in 175,872 visits per year. These visits support over 200 local jobs and result in $16.7 million direct spending to visit these lakes. Anglers spent 35,591 hours fishing the Creston area lakes in 2016 with an average trip cost of $142/trip. Fishing was the top reason for visiting the Creston area lakes. However, water quality is also a top factor affecting the choice of which lake to visit in Iowa.
Three-Mile Lake has a diverse sportfish population with Bluegill Lepomis macrochirus, Black Crappie Pomoxis nigromaculatus, White Crappie Pomoxis annularis, Redear Sunfish Lepomis microlophus, Largemouth Bass Micropterus salmoides, Smallmouth Bass Micropterus dolomieu, Walleye Sander vitreus, hybrid striped bass Morone saxatilis x Morone chrysops, and Blue Catfish Ictalurus furcatus available to anglers. Unfortunately two undesirable species, Common Carp Cyprinus carpio and Yellow Bass Morone mississippiensis are still present in the lake despite recent attempts to eradicate these species from the lake. Three-Mile Lake is stocked annually with Walleye, hybrid striped bass, and Blue Catfish. The introduction of Blue Catfish was initiated to create a unique trophy catfish fishery for anglers. A project evaluating the introduction is underway, but so far small numbers of large Blue Catfish are available to anglers (see Figure 2; 8.8 lb Blue Catfish sampled in 2018).
Staff from the Iowa DNR’s Mount Ayr Fish Management Station conducted a comprehensive fish sampling survey in 2021 which incorporates spring electrofishing, summer baited hoop nets, and fall fyke nets to evaluate the fishery. Spring electrofishing indicated moderate abundance of Largemouth Bass up to 19 inches are available to anglers. Good numbers of Walleye are also available to anglers especially in the 13-16 inch length range. Fall fyke netting indicated moderate abundance of Bluegill and Crappie species. Most of Bluegill were in the 7-9 inch length range. Crappies were mostly in the 9-11 inch length range. Blue Catfish were sampled in low abundance, but some large (8 lbs. +) Blue Catfish are available to anglers. Only a few hybrid striped bass were sampled in 2021.
Threats
Three-Mile Lake’s 23,730 acre watershed stretches across two rural southern Iowa counties, Adair County and Union County. Similar to other Iowa reservoirs, Three-Mile Lake is nestled within a highly agricultural landscape.
A land-use survey completed by the Natural Resource Conservation Service in 2018 revealed that 60% of the Three-Mile Lake watershed is currently in corn and soybean production, 30% pasture, and the remainder is woodlands, confined feeding operations, feedlots, and buildings. Expectedly, the lake’s water quality issues are derived from non-point pollution sources from the watershed especially sediment erosion, excess nutrients and pesticides, and bacteria from livestock operations.
What FOR Is Doing
The Three-Mile Lake restoration project began in 2016. The water level was lowered 15 feet below normal pool and promiscuous fishing was permitted in preparation for a fall fish renovation. Rotenone was applied in September 2016 to eradicate Common Carp Cyprinus carpio and Yellow Bass Morone mississippiensis that negatively impacted the water quality and sportfish quality of Three-Mile Lake. While the lake level was lowered during the winter of 2016-2017 members of the High Lakes Outdoor Alliance and Iowa DNR staff constructed 40 new cedar tree brushpiles and created rockpiles using donated materials for fish habitat. Additionally, over two miles of shoreline were re-armored with Class E riprap to prevent wind/wave shoreline erosion. All ten fishing jetties with re-armored with Class E riprap and road rock was placed on top to improve shoreline fishing access for anglers. Union County Conservation Board constructed two new sediment retention structures on public land to improve sediment and nutrient retention within the watershed (Figure 3). After the 2016 fish renovation and first phase of in-lake fish habitat improvements the lake was refilled in 2017.
Since the 2016 fish renovation, the Three-Mile Lake stakeholders have developed a comprehensive lake restoration plan to address the non-point pollution sources (e.g. sedimentation) affecting the lake’s water quality and plan to improve the quality of fish habitat available to sportfish in the lake. First, a watershed assessment was conducted by the Natural Resource Conservation Service in 2018 to determine current land-use practices in the watershed and identify priority areas for best management practices for sediment/nutrient retention (Figure 4). The assessment revealed that sediment delivery is more severe in the upper end of the watershed (Figure 5). Additionally, the upper end of the watershed has fewer catchment basins and existing best management practices implemented for sediment and nutrient retention (Figure 6). The assessment of the main tributary of Three-Mile Lake (aka Three-Mile Creek) had streambank heights of 6-15 feet and areas of bare of overhanging vegetation which can lead to increased streambank erosion during rain events (Figure 7). The increased streambank erosion could lead to increased turbidity in the lake.
After the 2018 watershed assessment, the Iowa DNR began to work with a private engineering firm, FYRA Engineering Inc., to identify additional restoration practices that can be implemented within the watershed as well as in-lake improvements that can lessen sedimentation from the lake’s agriculture-intensive watershed and ultimately improve the lake’s water quality. Two new embankments will be constructed in critical areas of the Three-Mile Lake Wildlife Management Area (WMA). Three existing ponds on the Three-Mile Lake WMA will be dredged to increase capacity for sediment retention. Three-Mile Lake has a large (25 acres) sediment/nutrient retention basin at the upper end of the reservoir. However, over time this basin has become full of sediment that is beginning to spill over into the lake. FYRA is investigating options to improve this structure either through targeted dredging, raising the elevation of the silt dam, or constructing a secondary silt basin below the existing structure. The option selected to improve this important structure will depend on United States Army Corps of Engineers permitting as well as available funding. Two additional in-lake silt basins will also be constructed in reservoir tributaries that receive considerable sediment/nutrient delivery (Figure 8).
In addition to the sediment catchment basins, the Three-Mile Lake stakeholders plan to prevent shoreline erosion into the lake due to wind and wave action. Shoreline erosion can lead to increased turbidity and negatively impact the lake’s water quality. The water level will be lowered by a maximum of 12 feet beginning in fall 2022 for shoreline improvements. Many areas of the shoreline are eroding into the lake leading to water clarity issues. Over 1,300 feet of shoreline in critical need of repair will be deepened and armored with Class E rip rap. An additional up to 13,000 feet of shoreline will be armored with Class E rip rap to prevent future shoreline erosion into the lake. Fishing jetties are popular locations for shoreline anglers to access the lake. Two of the 10 existing fishing jetties will be extended and three of the fishing jetties will be benched to create improved shoreline fishing opportunities for anglers.
Fish habitat is an important component of reservoir fish management. Sportfish need a diversity of fish habitat for spawning, foraging, cover from predators, and winter and summer refuge. Some fish habitat structures (ie. dirt mounds, rockpiles, cedar tree brushpiles) were constructed when Three-Mile Lake was constructed in the early 1990’s. In 2016-2017, cedar tree brushpiles and rockpiles were added to the lake using donated materials. However, quality fish habitat is still lacking at Three-Mile Lake especially rock structures. The rock structures create small crevices that attract aquatic invertebrates. Aquatic invertebrates are an important food source for fish therefore fish are attracted to the structures. These structures can improve fishing success for anglers as well. While the lake is lowered in 2022-2024, rock fish habitat structures including 30 gravel spawning areas (Figure 9a), 20 rockpiles, 10 rock fields (Figure 9b), 10 rock reefs (Figure 9c), and five extra wide rock reefs will be constructed to improve rock fish habitat in the lake. Overall these fish habitat enhancements will improve the quality of fish habitat available to sportfish in Three-Mile Lake and improve fishing success for anglers by acting as “fish attractors.”
Monitoring Plan
The Iowa DNR’s Fisheries Research section conducted an angler creel survey on Three-Mile Lake from 2015 (pre-fish renovation) to 2021 (post-fish renovation) to evaluate the effects of the fish renovation. Angler fishing effort and total catch has increased since the fish renovation in 2016 (Figure 10). Additionally, the composition of the angler’s catch has also changed since the fish renovation in 2016. Popular sportfish such as Bluegill, Crappie Pomoxis spp., and Walleye now comprise more of the angler’s harvest than prior to the fish renovation (Figure 11).
The Iowa DNR’s Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment Section conducts water quality sampling on 130 lakes each summer including Three-Mile Lake. The lake is sampled three times from May through September each year to evaluate a variety of water quality parameters (data is available on the AQuIA database (programs.iowadnr.gov/aquia). These data can be compared pre- and post-restoration to detect changes in the lake’s quality as a result of the restoration efforts (Figure 12).
Staff from the Iowa DNR’s Mount Ayr Fish Management Station will continue to evaluate the fish population after the restoration activities are implemented. Staff will continue to perform standard annual fish sampling using spring electrofishing and fall fyke netting to evaluate the Largemouth Bass, Bluegill, and Crappie spp. populations. Staff also conducts supplemental fish sampling using a variety of fish sampling gear (e.g. gill nets, hoop nets, float lines, low-frequency electrofishing) to evaluate the Blue Catfish introduction.
Outreach Plan
Since 2016, the Iowa DNR and stakeholders have assembled annually in-person or virtually to discuss restoration project successes and setbacks at Three-Mile Lake. Small follow-up meetings with project stakeholders occur as needed to ensure the restoration project is moving forward. During the fish renovation in 2016, a Three-Mile Lake FAQ document was developed and provided to anglers by the Iowa DNR creel clerk for anyone with questions about the project.
Fishing success has increased since the fish renovation in 2016. Pictures of anglers with their catch have been posted on all of the Iowa DNR social media platforms. This will continue as the restoration project continues to celebrate restoration project successes.
The Iowa DNR will host a public meeting in summer 2022 to discuss the next phase of restoration activities. This will include the water level draw-down for in-lake improvements such as shoreline armoring and in-lake fish habitat. The meeting will be held at Southwestern Community College with state of the art technology resources and a large conference room to host many community members interested in the project both in person and virtually if necessary.
Related News

Project Information Available for FY2023 Approved Grants
Want to learn more about the FY2023 Approved Projects? Friends of Reservoirs has five large grant projects funded this year. Learn more about them, and please reply with any questions! […]

Bass Pro Shops/National Fish Habitat Partnership U.S. Open Grant Program Funds Nine Projects in 2022
(Washington, DC) - The National Fish Habitat Partnership (NFHP) announced today nine projects funded through a nearly $1.6 million grant program established through proceeds from the Bass Pro Shops U.S. Open […]
Donate Today
to support similar habitat projects